PySide2
界面布局 Layout
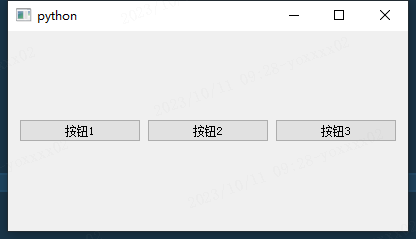
QHBoxLayout 水平布局
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
class Window(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
button1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮1', self)
button2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮2', self)
button3 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮3', self)
# 创建layout对象,并且添加内部控件
hl = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
hl.addWidget(button1)
hl.addWidget(button2)
hl.addWidget(button3)
# 指定容器控件自身使用的layout
self.setLayout(hl)
app = QtWidgets.QApplication()
window = Window()
window.resize(400, 200)
window.show()
app.exec_()
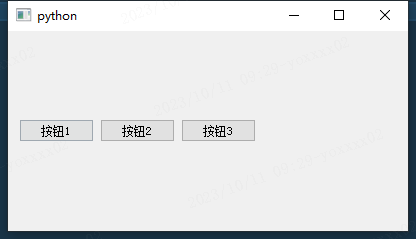
# 剩余空间弹性布局
hl.addStretch()
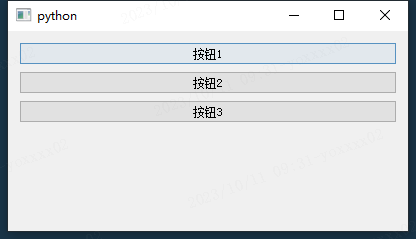
QVBoxLayout 垂直布局
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
class Window(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
button1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮1', self)
button2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮2', self)
button3 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮3', self)
# 创建layout对象,并且添加内部控件
vl = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
vl.addWidget(button1)
vl.addWidget(button2)
vl.addWidget(button3)
vl.addStretch()
# 指定容器控件自身使用的layout
self.setLayout(vl)
app = QtWidgets.QApplication()
window = Window()
window.resize(400, 200)
window.show()
app.exec_()
QGridLayout 表格布局
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
class Window(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
button1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮1', self)
button2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮2', self)
button3 = QtWidgets.QPushButton('按钮3', self)
# 创建一个水平layout作为内部layout
gl = QtWidgets.QGridLayout()
gl.addWidget(button1, 0, 0) # 添加到第1行,第1列
gl.addWidget(button2, 0, 1) # 添加到第1行,第2列
gl.addWidget(button3, 1, 1) # 添加到第2行,第2列
# 指定自身使用的layout
self.setLayout(gl)
app = QtWidgets.QApplication([])
window = Window()
window.resize(400, 200)
window.show()
app.exec_()

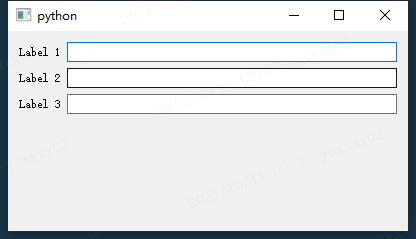
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
class Window(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
fl = QtWidgets.QFormLayout()
fl.addRow(QtWidgets.QLabel("Label 1"), QtWidgets.QLineEdit())
fl.addRow(QtWidgets.QLabel("Label 2"), QtWidgets.QLineEdit())
fl.addRow(QtWidgets.QLabel("Label 3"), QtWidgets.QLineEdit())
# 指定自身使用的layout
self.setLayout(fl)
app = QtWidgets.QApplication([])
window = Window()
window.resize(400, 200)
window.show()
app.exec_()
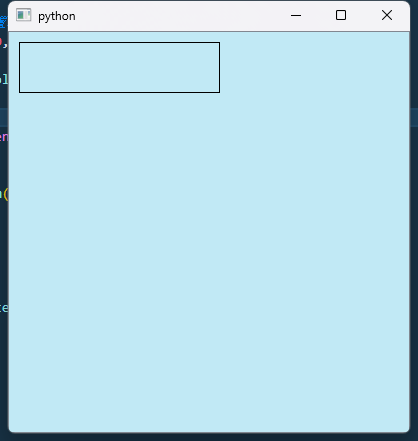
Graphic View
简单示例
- QGraphicsScene 画布
- QGraphicsView 展示层
- QGraphicsItem 元素, 控制层
from PySide2 import QtWidgets, QtGui
app = QtWidgets.QApplication()
# 创建 QGraphicsScene 对象, 设置位置和高度宽度
scene = QtWidgets.QGraphicsScene(0, 0, 400, 400)
# 设置背景色
scene.setBackgroundBrush(QtGui.QColor('#C1E9F5'))
# 创建 QGraphicsView 对象
view = QtWidgets.QGraphicsView(scene)
# 创建矩形对象
rect = QtWidgets.QGraphicsRectItem(10, 10, 200, 50)
# 添加到 QGraphicsScene 中
scene.addItem(rect)
# 允许移动
rect.setFlag(QtWidgets.QGraphicsItem.ItemIsMovable, True)
view.show()
app.exec_()
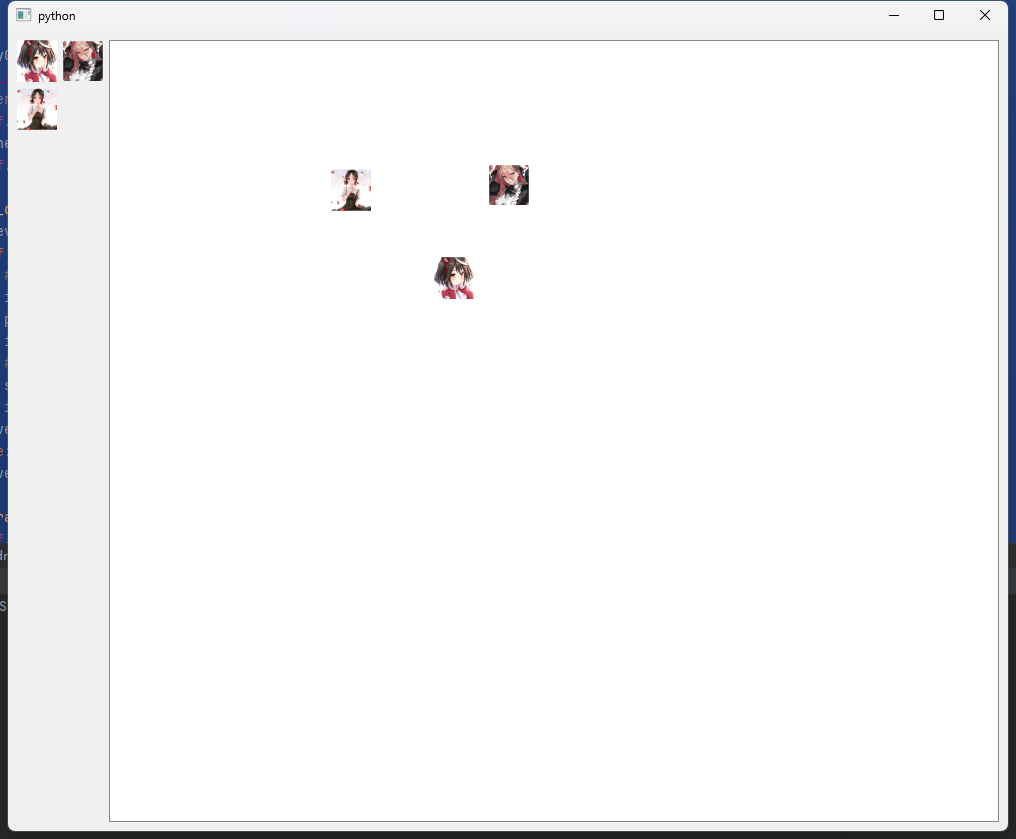
两侧布局并支持拖拽
from PySide2 import QtWidgets, QtGui, QtCore
PIC_LIST = ["1", "2", "3"]
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 1000, 800
class DraggableLabel(QtWidgets.QLabel):
def __init__(self, parent=None, image_path=None):
super(DraggableLabel, self).__init__(parent)
# 加载图片
pixmap = QtGui.QPixmap(image_path)
# 设定图片缩放大小, 高度等比缩放
pixmap = pixmap.scaledToWidth(40, QtCore.Qt.SmoothTransformation)
# 设置label的图片
self.setPixmap(pixmap)
self.setAcceptDrops(True) # 设置可接受拖拽
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
if event.button() == QtCore.Qt.LeftButton:
# 创建拖拽对象
drag = QtGui.QDrag(self)
mime_data = QtCore.QMimeData()
mime_data.setImageData(self.pixmap().toImage()) # 设置拖拽的图片数据
drag.setMimeData(mime_data)
drag.exec_(QtCore.Qt.CopyAction)
class MyGraphicsView(QtWidgets.QGraphicsView):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(MyGraphicsView, self).__init__(parent)
self.setAcceptDrops(True) # 设置可接受拖拽
scene = QtWidgets.QGraphicsScene(0, 0, int(WIDTH * 0.8), int(HEIGHT * 0.8))
self.setScene(scene)
def __drag(self, action, event):
if event.mimeData().hasImage():
if action == "drop":
# 在GraphicsView中显示拖拽的图片
image = event.mimeData().imageData()
pixmap = QtGui.QPixmap.fromImage(image)
item = self.scene().addPixmap(pixmap)
# 将坐标转换为场景坐标
scene_pos = self.mapToScene(event.pos())
item.setPos(scene_pos)
event.accept()
else:
event.ignore()
def dragEnterEvent(self, event):
self.__drag("enter", event)
def dragMoveEvent(self, event):
self.__drag("move", event)
def dropEvent(self, event):
self.__drag("drop", event)
class MWindow(QtWidgets.QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.resize(WIDTH, HEIGHT)
centralWidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(self)
self.setCentralWidget(centralWidget)
# 设置水平布局
self.mainLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout(centralWidget)
self.setupLeftPane() # 左边区域
self.setupCanvas() # 右边区域
def setupLeftPane(self):
gl = QtWidgets.QGridLayout()
for index, name in enumerate(PIC_LIST):
row, col = int(index / 2), index % 2
label = DraggableLabel(image_path=f"./images/{name}.png")
gl.addWidget(label, row, col)
# 添加左侧的布局到主布局
leftLayout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
leftLayout.addLayout(gl)
leftLayout.addStretch()
self.mainLayout.addLayout(leftLayout)
def setupCanvas(self):
self.view = MyGraphicsView()
# 添加绘制组件到主布局
self.mainLayout.addWidget(self.view)
def main():
app = QtWidgets.QApplication()
# 对于显示器使用缩放图片的, 加上这一句使得图片不毛糙
app.setHighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy(QtCore.Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.Round)
window = MWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()